U tube lab glass with side arms
A U-tube lab glass with side arms is a specialized piece of laboratory glassware characterized by its U-shaped design, which allows for versatile applications in chemical experiments. The main body of the U-tube features two vertical arms connected at the bottom, with additional side arms that extend horizontally. These side arms are typically fitted with ground glass joints or stoppers, enabling easy connection to other apparatus.
Universal pH chart 1 to 14
A Universal pH chart is a visual tool used to determine the pH level of a solution, indicating its acidity or alkalinity. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Values below 7 indicate acidity, while values above 7 indicate alkalinity. The chart is typically color-coded, with each color corresponding to a specific pH value.
How to Use the Universal pH Chart:
- Obtain a pH indicator: This can be in the form of pH paper strips or a liquid pH indicator solution.
- Test the solution: Dip the pH paper strip into the solution or add a few drops of the liquid indicator to the solution.
- Observe the color change: The pH paper or solution will change color based on the pH level of the solution.
- Compare the color: Match the resulting color to the corresponding color on the Universal pH chart to determine the pH value of the solution.
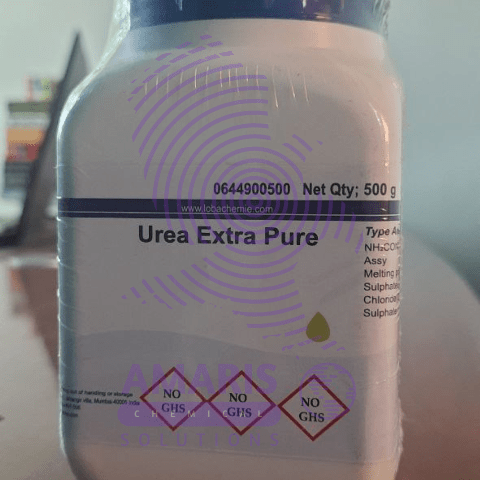
Urea 500gm
Urea is an organic compound with the chemical formula CO(NH₂)₂. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic. Here are some key points about urea:
Chemical Properties:
- Formula: CO(NH₂)₂
- Molecular Weight: 60.06 g/mol
- Structure: Urea consists of two amine groups (-NH₂) attached to a carbonyl group (C=O).
Production:
Urea is primarily produced via the Haber-Bosch process, which synthesizes ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen. The ammonia is then combined with carbon dioxide to form urea: 2NH3+CO2→CO(NH2)2+H2O2 text{NH}_3 + text{CO}_2 rightarrow text{CO(NH}_2text{)}_2 + text{H}_2text{O}2NH3+CO2→CO(NH2)2+H2OVacuum and air pressure pump combined
Combining a vacuum pump with an air pressure pump in a laboratory setting can offer versatile control over atmospheric conditions within experimental setups. Here's how they can be used together:
- Vacuum Pump: A vacuum pump removes air or gas molecules from a sealed chamber, creating a vacuum or low-pressure environment. This is useful for various laboratory applications such as:
- Removing air from containers or chambers to create a vacuum for experiments involving gases or vacuum-distillation techniques.
- Evacuating air from reaction vessels to prevent unwanted reactions with oxygen or moisture.
- Facilitating the transfer of liquids through vacuum filtration systems.
- Assisting in the operation of vacuum ovens or freeze dryers for sample preparation or preservation.
- Air Pressure Pump: An air pressure pump, also known as a compressor, increases the pressure of air or gas within a system. In a laboratory, it can be employed for tasks like:
- Supplying compressed air for pneumatic equipment or instruments requiring air-driven operation.
- Pressurizing reaction vessels or chambers for experiments requiring elevated pressures, such as high-pressure chemical synthesis or hydrothermal reactions.
- Generating pressure differentials for applications like air-powered suction or sample manipulation.
- Facilitating gas exchange in bioreactors or fermenters used for cell culture or microbial growth.
- In materials science, they might be used to manipulate the environment during thin-film deposition processes.
- In chemistry, they could be employed for vacuum distillation followed by pressurized reactions.
- In biology, they might facilitate the controlled atmosphere required for tissue culture or cell incubation experiments.
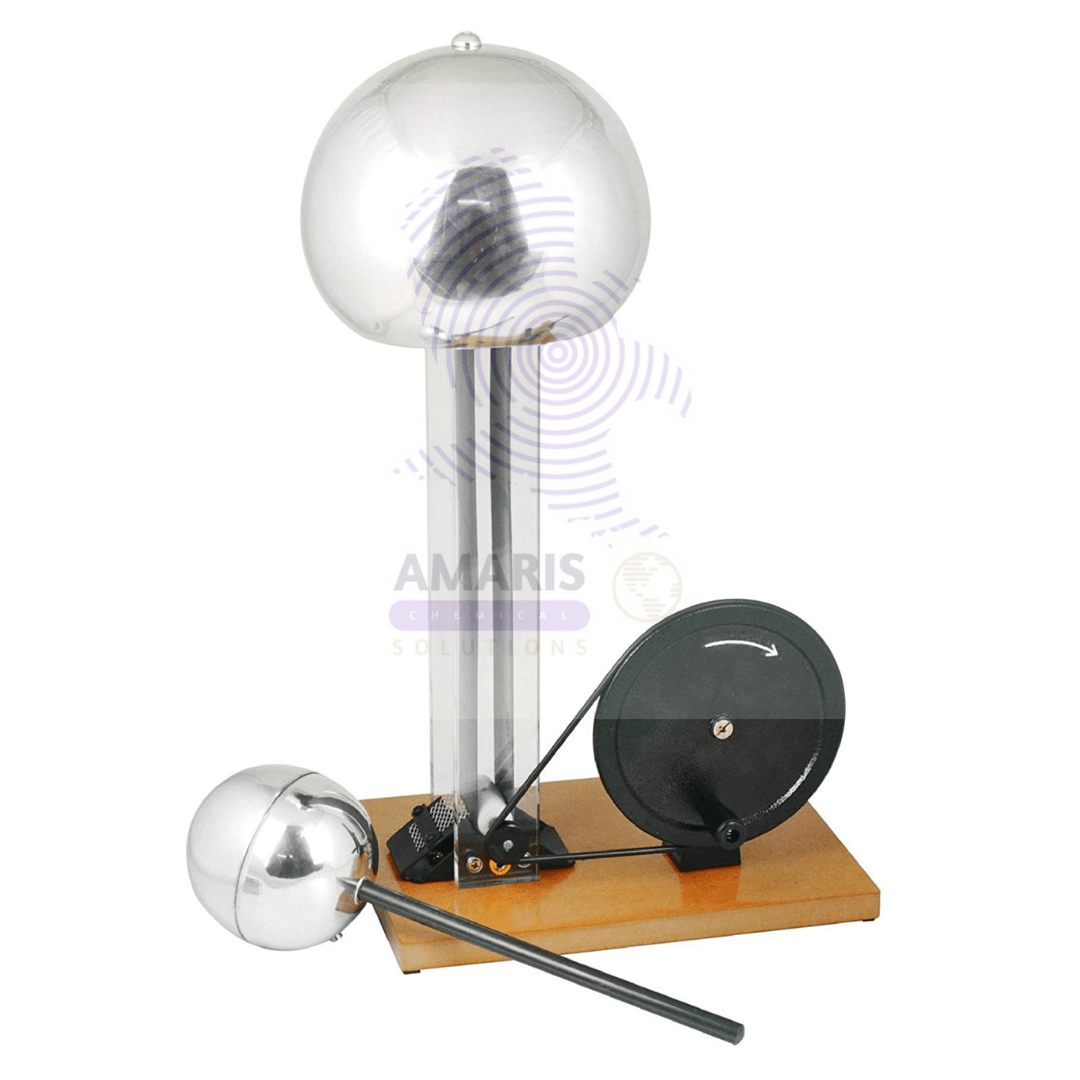
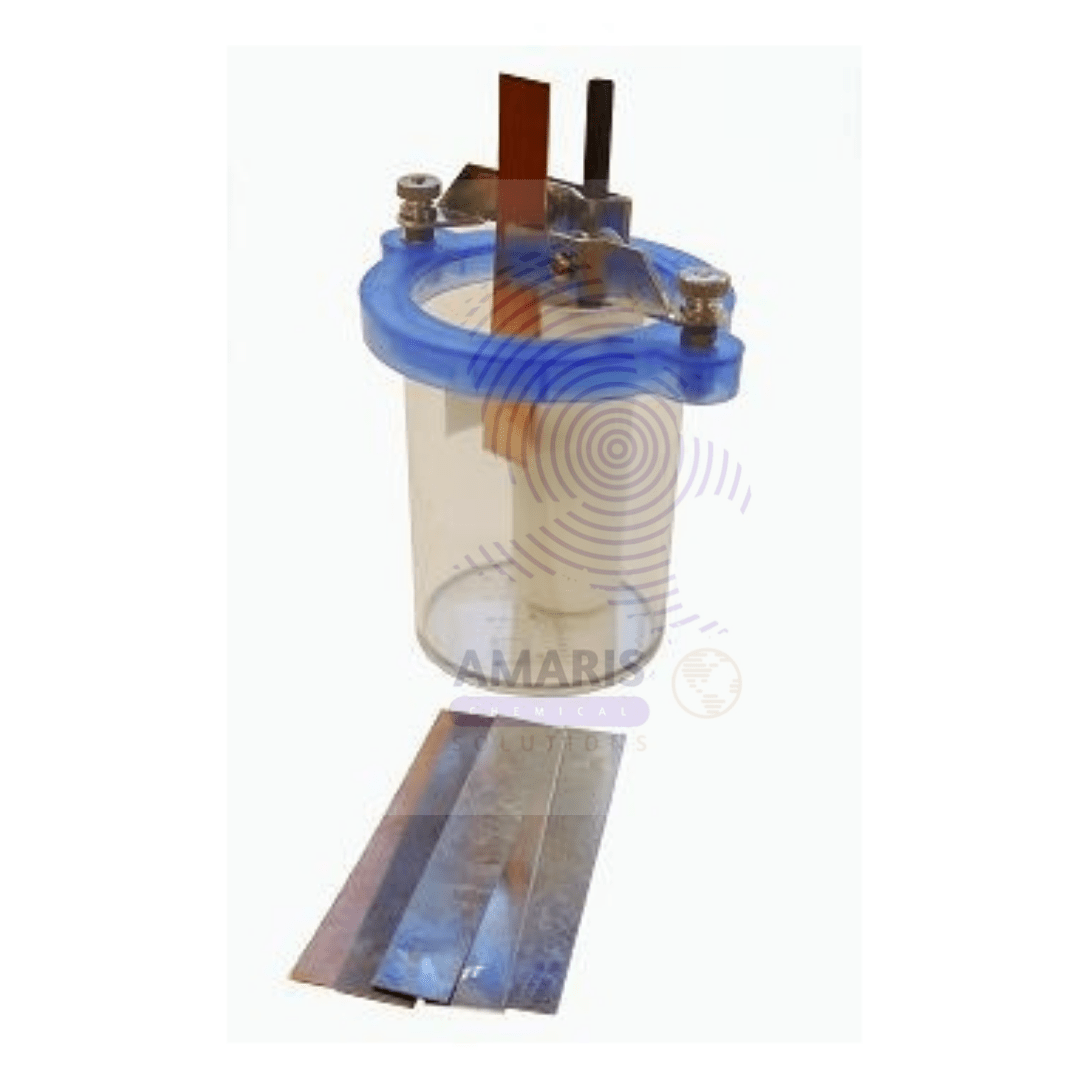
Van de generator manual
Van de graaf generator electrical
Van de Graaff generators are fascinating pieces of equipment commonly used in physics laboratories and educational settings to demonstrate principles of electrostatics. Here's how they work and some of their uses:
How Van de Graaff Generators Work:
- Charge Accumulation: The generator consists of a large, hollow metal sphere mounted on top of an insulated column. Inside the column, there's a moving belt made of insulating material, usually rubber or plastic. This belt is driven by a motor, moving continuously upward.
- Frictional Charging: As the belt moves, it rubs against two rollers or combs at the bottom and top of the column. This friction causes the belt to acquire a large amount of positive charge.
- Charge Transfer: The charge on the belt is carried upwards and transferred to the metal sphere at the top of the column. Since the sphere is conductive, the charge spreads evenly across its surface due to electrostatic repulsion, creating a very high voltage.
- Electric Potential: This process creates a large electric potential between the sphere and the ground, sometimes reaching hundreds of thousands or even millions of volts.
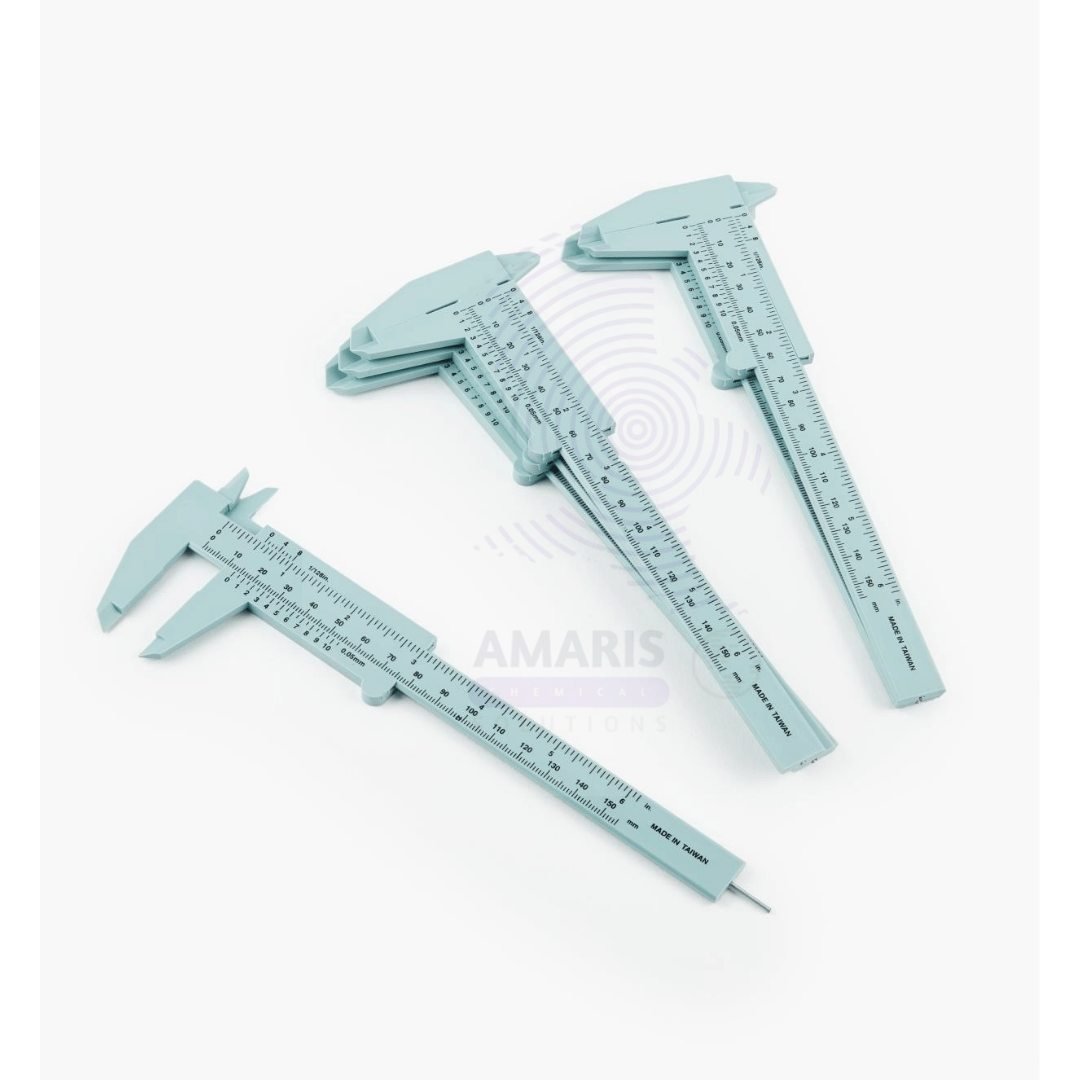
Vennier callipers
Vernier calipers are indeed commonly used in laboratory settings for various measurement tasks. These precision instruments are particularly handy for measuring dimensions with high accuracy, especially when it comes to small objects or components. Here's how they're typically used in a laboratory:
- Measurement of Length: Vernier calipers are primarily used to measure the length, diameter, or thickness of objects with high precision. This could include measuring the dimensions of small components, specimens, or samples in experiments.
- Internal and External Measurements: They can measure both internal and external dimensions of objects. For instance, you could use them to measure the diameter of a test tube (external measurement) or the diameter of a hole (internal measurement).
- Accuracy: Vernier calipers offer high accuracy, typically down to fractions of a millimeter or even less, depending on the instrument's precision. This level of accuracy is crucial in many laboratory experiments and quality control processes.
- Versatility: They're versatile instruments that can measure various types of objects, including round, square, or irregularly shaped ones.
- Depth Measurement: Some Vernier calipers also have a depth gauge attachment, allowing for precise depth measurements, which can be crucial in certain experiments or when working with objects that require precise depth control.
- Zero Error Correction: Proper use of Vernier calipers involves ensuring there is no zero error, meaning the jaws are closed and the zero on the Vernier scale aligns perfectly with the zero on the main scale. This ensures accurate measurements.
- Material Analysis: In materials science laboratories, Vernier calipers can be used to measure the thickness of materials such as films, coatings, or sheets.
- Experimental Setup: They're often utilized in experimental setups where precise measurements are required for ensuring the accuracy and reproducibility of results.
Visking Tube 1 Metre
A Visking tube, also known as dialysis tubing, is a type of semi-permeable membrane tubing used in various scientific and medical applications. It is commonly used in biological and chemical laboratories for processes such as dialysis, osmosis, and diffusion studies.
Key Features of Visking Tube:
- Semi-permeable Membrane: Visking tubes allow certain small molecules and ions to pass through while blocking larger molecules. This property makes them ideal for separating substances based on size.
- Composition: Typically made from cellulose or regenerated cellulose, which provides the selective permeability required for its functions.
- Applications:
- Dialysis: Used to separate small molecules or ions from larger molecules in solution, commonly used in protein purification.
- Osmosis Experiments: Demonstrates osmosis, a process where water moves across the membrane from a region of low solute concentration to a region of high solute concentration.
- Educational Demonstrations: Frequently used in classrooms to demonstrate principles of diffusion and osmosis.
How It Works:
- Dialysis: The Visking tube is filled with a solution containing both small and large molecules and then submerged in a solvent. Over time, the small molecules pass through the membrane into the surrounding solvent, while the larger molecules are retained inside the tube.
- Osmosis: When filled with a concentrated solution and placed in pure water, water will move into the tube, increasing the volume inside, demonstrating osmotic pressure.
Practical Considerations:
- Preparation: The Visking tube must be soaked in water before use to make it flexible and remove any preservatives.
- Clamping: Both ends of the tube need to be securely clamped or tied to prevent leakage during experiments.
Educational Value:
- Visking tubes are valuable educational tools in demonstrating fundamental biological processes like nutrient absorption, waste excretion, and fluid balance in cells.
Example Experiment:
- Diffusion of Glucose and Starch: Fill the Visking tube with a solution of glucose and starch, then immerse it in water containing iodine. Over time, glucose will diffuse out of the tube while starch remains inside, demonstrating selective permeability.
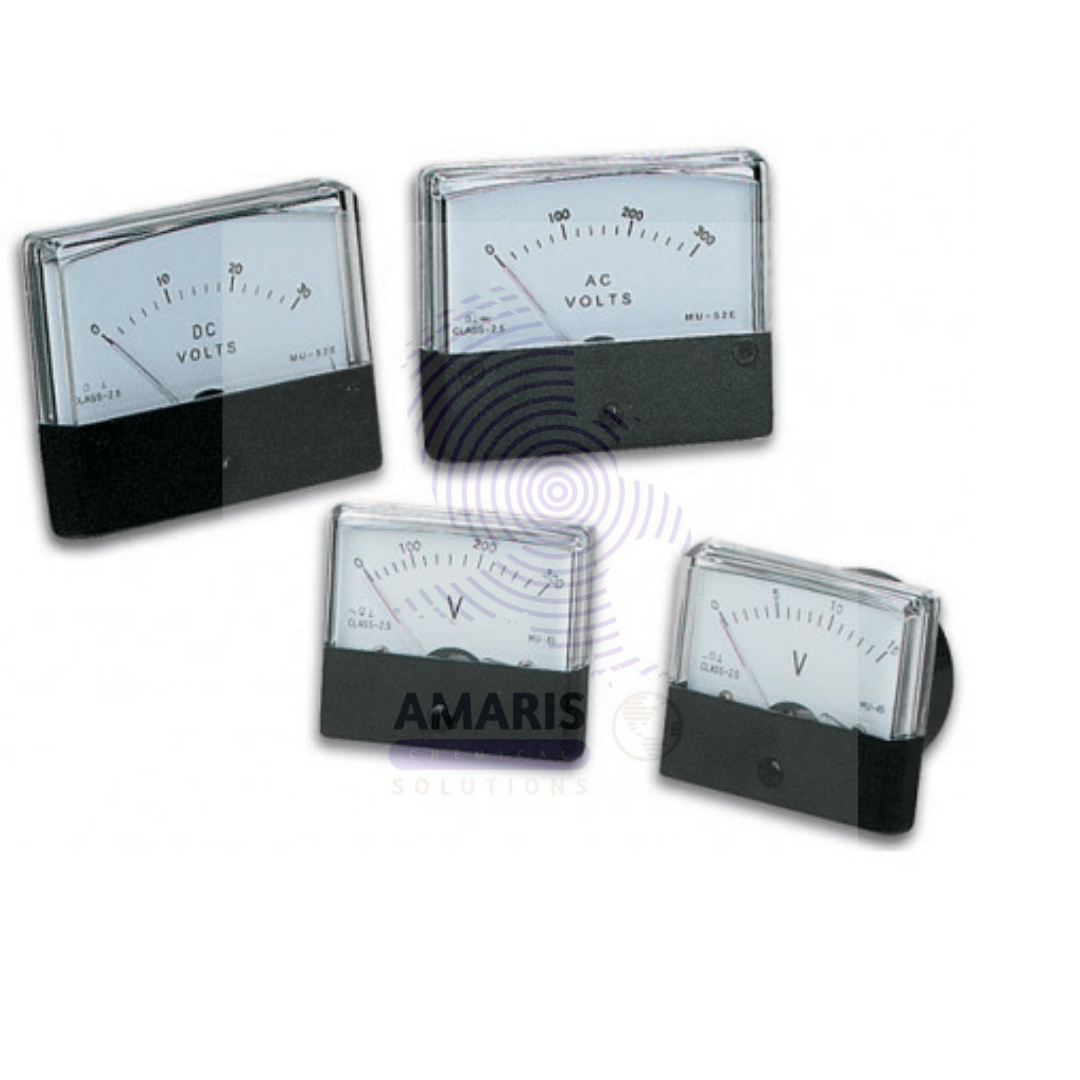
Voltmeter 30v electric and dual range
A voltmeter is an instrument used to measure voltage in electrical circuits. A voltmeter with a 30V electric dual range is versatile for laboratory use. It means it can measure voltage up to 30 volts, and it likely has multiple measurement ranges within that 30-volt range for increased accuracy and versatility.
The "dual range" feature typically means that the voltmeter has two separate measurement ranges. For instance, it might have a lower range (e.g., 0-10 volts) and a higher range (e.g., 0-30 volts). This allows you to select the appropriate range for the voltage you're measuring, ensuring that the instrument provides accurate readings.
In a laboratory setting, having a voltmeter with dual range capabilities can be beneficial because it allows for more precise measurements across a wider range of voltages, accommodating various experimental setups and electrical components.