Tuning fork set of 8
This high-quality tuning fork set includes eight precision-tuned forks, each crafted from durable aluminum for optimal resonance and clarity. Each fork is meticulously tuned to specific frequencies, ranging from low to high pitches, making it an essential tool for sound experiments, musical applications, and educational demonstrations. Ideal for studying sound waves, resonance, and interference patterns, this set is perfect for laboratory use, music classrooms, and audiology tests. The included storage case ensures easy organization and portability, making it a practical choice for both professionals and students.
U tube lab glass
U-tube lab glass, also known as a U-tube manometer, is a glass device shaped like the letter "U" that is primarily used for measuring pressure in gases and liquids. It consists of two vertical arms connected at the bottom, typically filled with a liquid (like water or mercury) that acts as a pressure reference. The difference in height between the two liquid columns indicates the pressure difference between the two points being measured.
U tube lab glass with side arms
A U-tube lab glass with side arms is a specialized piece of laboratory glassware characterized by its U-shaped design, which allows for versatile applications in chemical experiments. The main body of the U-tube features two vertical arms connected at the bottom, with additional side arms that extend horizontally. These side arms are typically fitted with ground glass joints or stoppers, enabling easy connection to other apparatus.
Universal pH chart 1 to 14
A Universal pH chart is a visual tool used to determine the pH level of a solution, indicating its acidity or alkalinity. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Values below 7 indicate acidity, while values above 7 indicate alkalinity. The chart is typically color-coded, with each color corresponding to a specific pH value.
How to Use the Universal pH Chart:
- Obtain a pH indicator: This can be in the form of pH paper strips or a liquid pH indicator solution.
- Test the solution: Dip the pH paper strip into the solution or add a few drops of the liquid indicator to the solution.
- Observe the color change: The pH paper or solution will change color based on the pH level of the solution.
- Compare the color: Match the resulting color to the corresponding color on the Universal pH chart to determine the pH value of the solution.
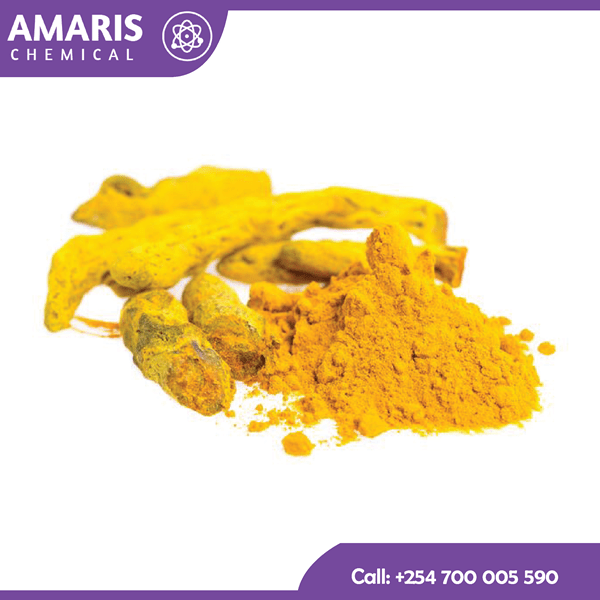
Urea 50 kg
Urea is an organic compound with the chemical formula CO(NH2)2. It is a crystalline substance that is highly soluble in water. Urea is produced naturally in the bodies of mammals as a byproduct of protein metabolism and is excreted in urine. It is also synthetically produced on a large scale for various industrial applications.
In simple terms, urea is a nitrogenous compound that contains two amine groups (-NH2) attached to a carbonyl group (C=O). It plays a crucial role in the nitrogen cycle, serving as a primary vehicle for the excretion of nitrogenous waste in mammals. Urea is commonly used as a fertilizer in agriculture due to its high nitrogen content, and it is also utilized in the production of plastics, resins, adhesives, and various other industrial applications.
Urea 500gm
Urea is an organic compound with the chemical formula CO(NH₂)₂. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic. Here are some key points about urea:
Chemical Properties:
- Formula: CO(NH₂)₂
- Molecular Weight: 60.06 g/mol
- Structure: Urea consists of two amine groups (-NH₂) attached to a carbonyl group (C=O).
Production:
Urea is primarily produced via the Haber-Bosch process, which synthesizes ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen. The ammonia is then combined with carbon dioxide to form urea: 2NH3+CO2→CO(NH2)2+H2O2 text{NH}_3 + text{CO}_2 rightarrow text{CO(NH}_2text{)}_2 + text{H}_2text{O}2NH3+CO2→CO(NH2)2+H2OVacuum and air pressure pump combined
Combining a vacuum pump with an air pressure pump in a laboratory setting can offer versatile control over atmospheric conditions within experimental setups. Here's how they can be used together:
- Vacuum Pump: A vacuum pump removes air or gas molecules from a sealed chamber, creating a vacuum or low-pressure environment. This is useful for various laboratory applications such as:
- Removing air from containers or chambers to create a vacuum for experiments involving gases or vacuum-distillation techniques.
- Evacuating air from reaction vessels to prevent unwanted reactions with oxygen or moisture.
- Facilitating the transfer of liquids through vacuum filtration systems.
- Assisting in the operation of vacuum ovens or freeze dryers for sample preparation or preservation.
- Air Pressure Pump: An air pressure pump, also known as a compressor, increases the pressure of air or gas within a system. In a laboratory, it can be employed for tasks like:
- Supplying compressed air for pneumatic equipment or instruments requiring air-driven operation.
- Pressurizing reaction vessels or chambers for experiments requiring elevated pressures, such as high-pressure chemical synthesis or hydrothermal reactions.
- Generating pressure differentials for applications like air-powered suction or sample manipulation.
- Facilitating gas exchange in bioreactors or fermenters used for cell culture or microbial growth.
- In materials science, they might be used to manipulate the environment during thin-film deposition processes.
- In chemistry, they could be employed for vacuum distillation followed by pressurized reactions.
- In biology, they might facilitate the controlled atmosphere required for tissue culture or cell incubation experiments.