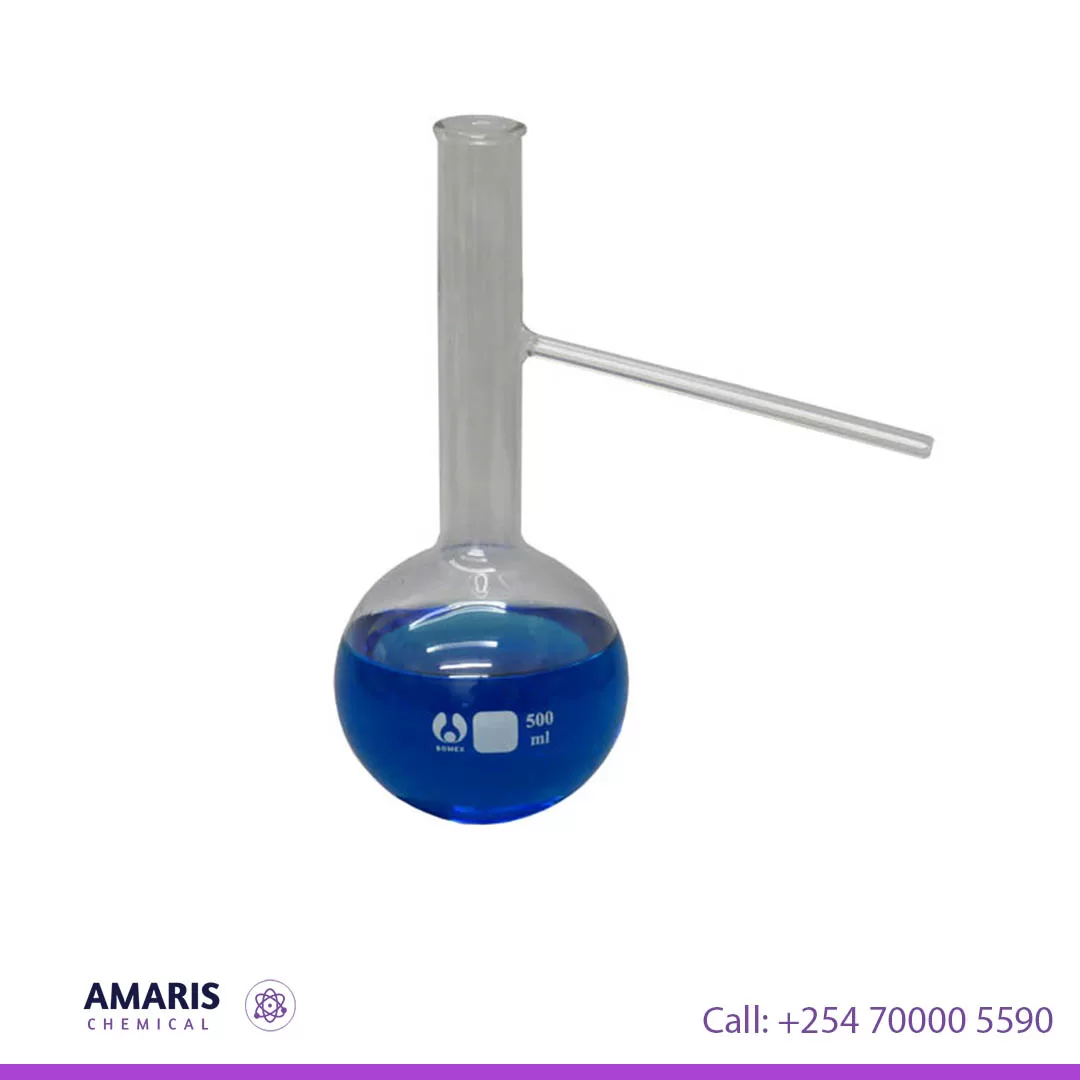
DOP (Dioctyl Phthalate) 200 kg drum
Dioctyl phthalate (DOP) is a clear, colorless liquid with a slightly fruity odor. It is a commonly used industrial chemical and a type of phthalate ester, which is a plasticizer. DOP is often added to plastics, such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC), to make them more flexible and easier to process. It is also used as a solvent and a lubricant in a variety of industrial and consumer applications. However, due to concerns about its potential health and environmental effects, DOP is being replaced by other plasticizers in many applications.
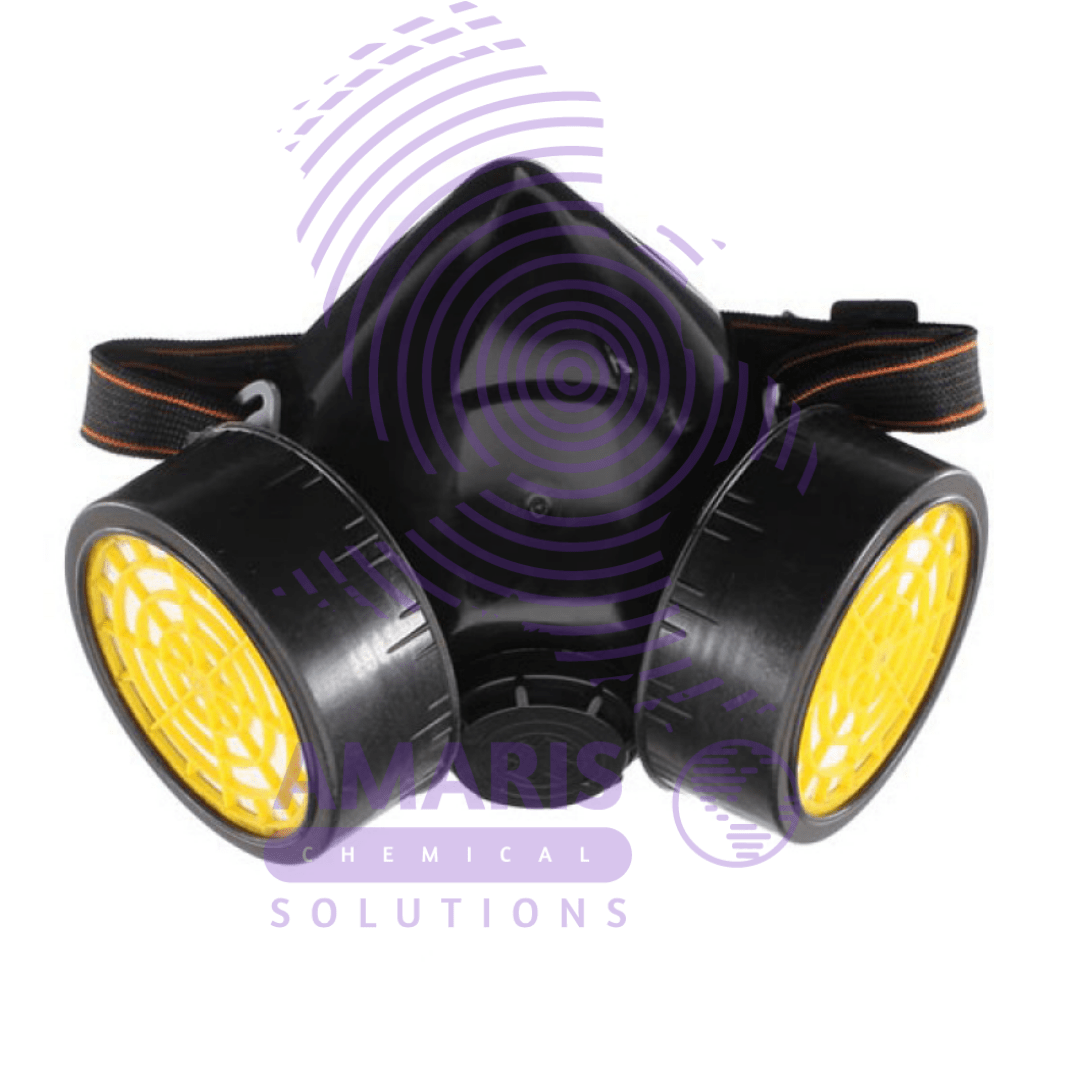
Double Gas Mask
A double gas mask, also known as a dual cartridge respirator, is commonly used in laboratories and industrial settings where there's a risk of exposure to hazardous gases, vapors, or particulates.
Here's how it works:
- Dual Cartridges: The mask has two cartridges, one on each side of the mask, which contain filters to purify the air. These cartridges are usually filled with activated charcoal or other filtering materials designed to absorb or neutralize specific chemicals or particulates.
- Seal: A proper seal between the mask and the wearer's face is crucial to ensure that no contaminated air can leak in. This seal is typically achieved through adjustable straps that secure the mask snugly against the face.
- Exhalation Valve: Most masks have an exhalation valve to allow the wearer to exhale easily without causing a buildup of moisture or CO2 inside the mask.
- Visibility: The mask is designed to provide adequate visibility while still offering protection. Some models have anti-fog features to prevent the visor from fogging up during use.
- Compatibility: Depending on the specific hazards in the environment, different types of cartridges can be used with the mask. These cartridges are often color-coded for easy identification.
- Fit Testing: It's essential for users to undergo fit testing to ensure that the mask provides an effective seal. Fit testing involves performing various exercises to check for any leaks around the mask's edges.
Double tripple single lab pulley
Single Lab Pulley: The simplest form, a single lab pulley consists of a wheel with a groove for a rope or cable. It allows for the vertical lifting of light loads with minimal friction. Ideal for basic lifting tasks and counterbalancing weights in laboratory experiments.
Double Lab Pulley: Featuring two wheels, this pulley system effectively doubles the lifting force. It provides a mechanical advantage, enabling heavier loads to be raised with less effort. The double pulley is perfect for applications requiring smooth operation and better control of lifted objects.
Triple Lab Pulley: With three wheels, the triple pulley system offers the highest mechanical advantage, allowing for the lifting of very heavy objects with ease. This complex setup is commonly used in advanced laboratory experiments, providing precision in controlling the height and weight of equipment or samples
Dropper bottle eyedrop
A dropper bottle, commonly referred to as an eyedropper bottle, is a small, typically transparent container made from glass or plastic, designed for dispensing liquids in controlled, precise amounts. It features a narrow neck with a dropper insert, which includes a rubber bulb or pipette that allows for easy suction and release of the liquid. This design makes it ideal for transferring small volumes of reagents, solutions, or other liquids in laboratory settings, pharmaceuticals, or personal care applications. Dropper bottles ensure accurate measurement and minimize spillage, making them essential tools for tasks ranging from scientific experiments to administering medications. They are available in various sizes and are often marked with graduated measurements for enhanced precision.
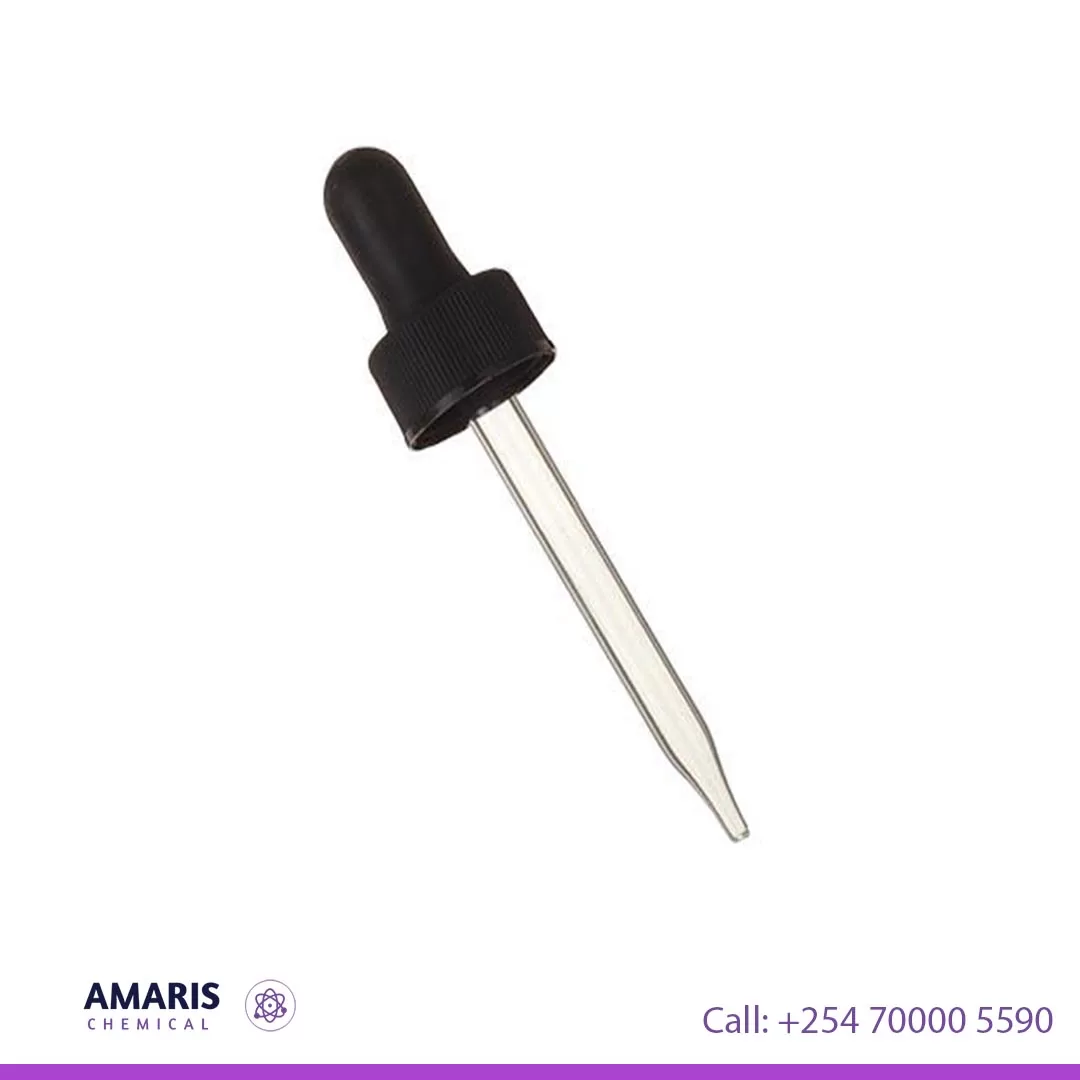
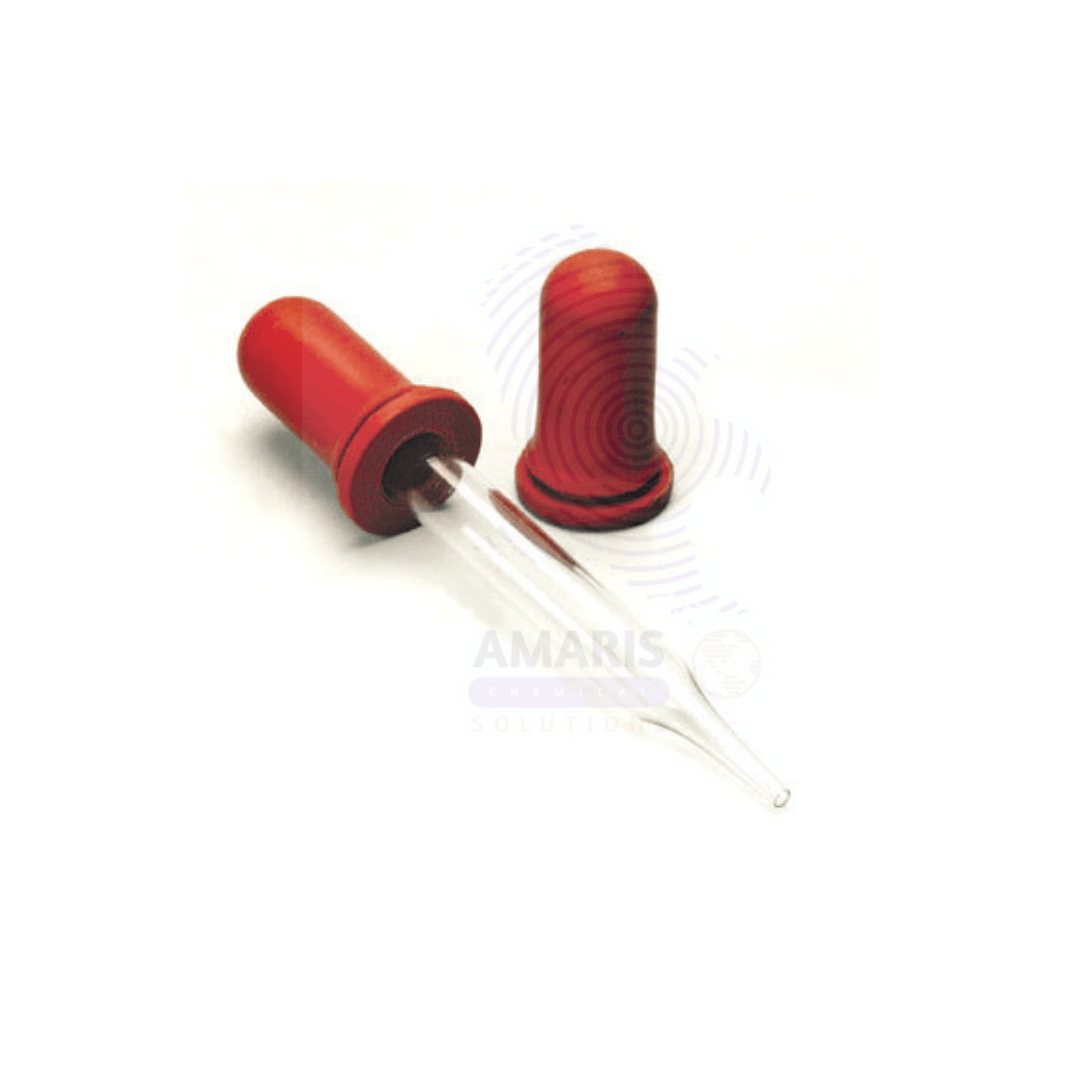
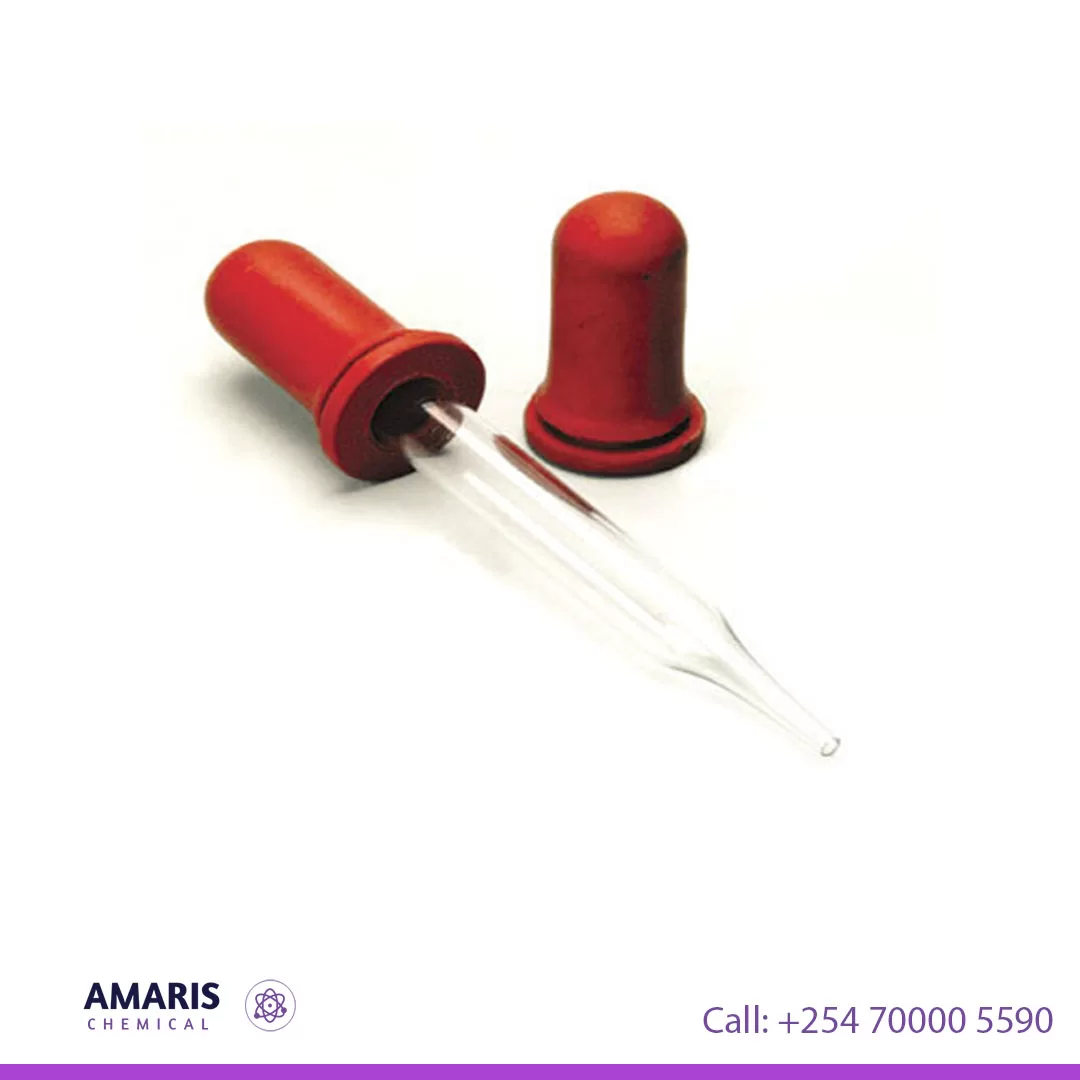
Dropper Teat
Dropper with teats
Dropper with teats
A dropper with a teat consists of a slender, graduated glass or plastic tube with a flexible rubber bulb (teat) at one end. The bulb allows for easy suction and release of liquid, enabling precise control over the volume dispensed. The tube often has graduated markings, allowing for approximate measurements of the liquid. This laboratory tool is essential for transferring small volumes of liquids, adding reagents dropwise, and conducting experiments requiring meticulous control over liquid delivery. Its design ensures minimal spillage and contamination, making it ideal for applications in chemistry, biology, and other scientific fields.