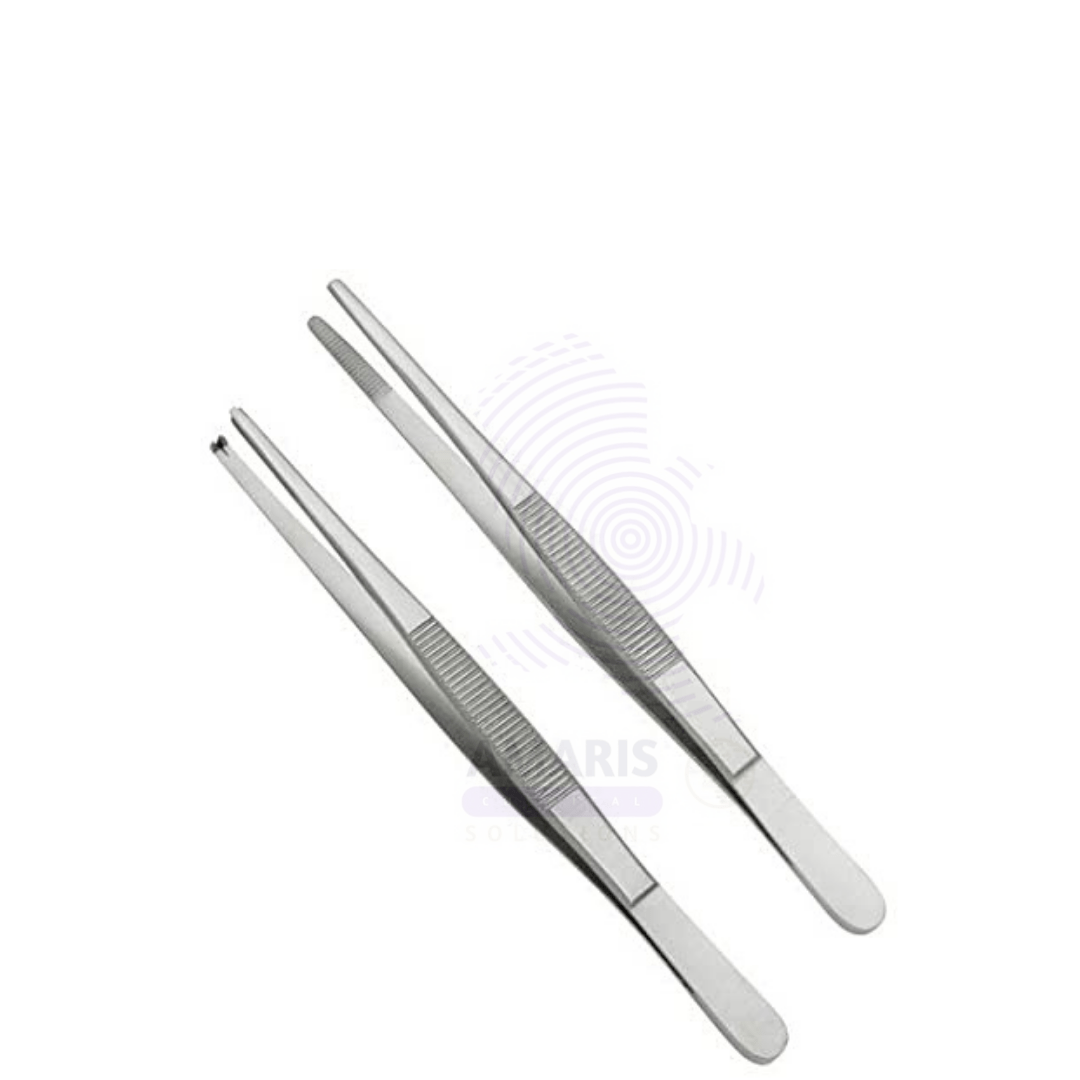
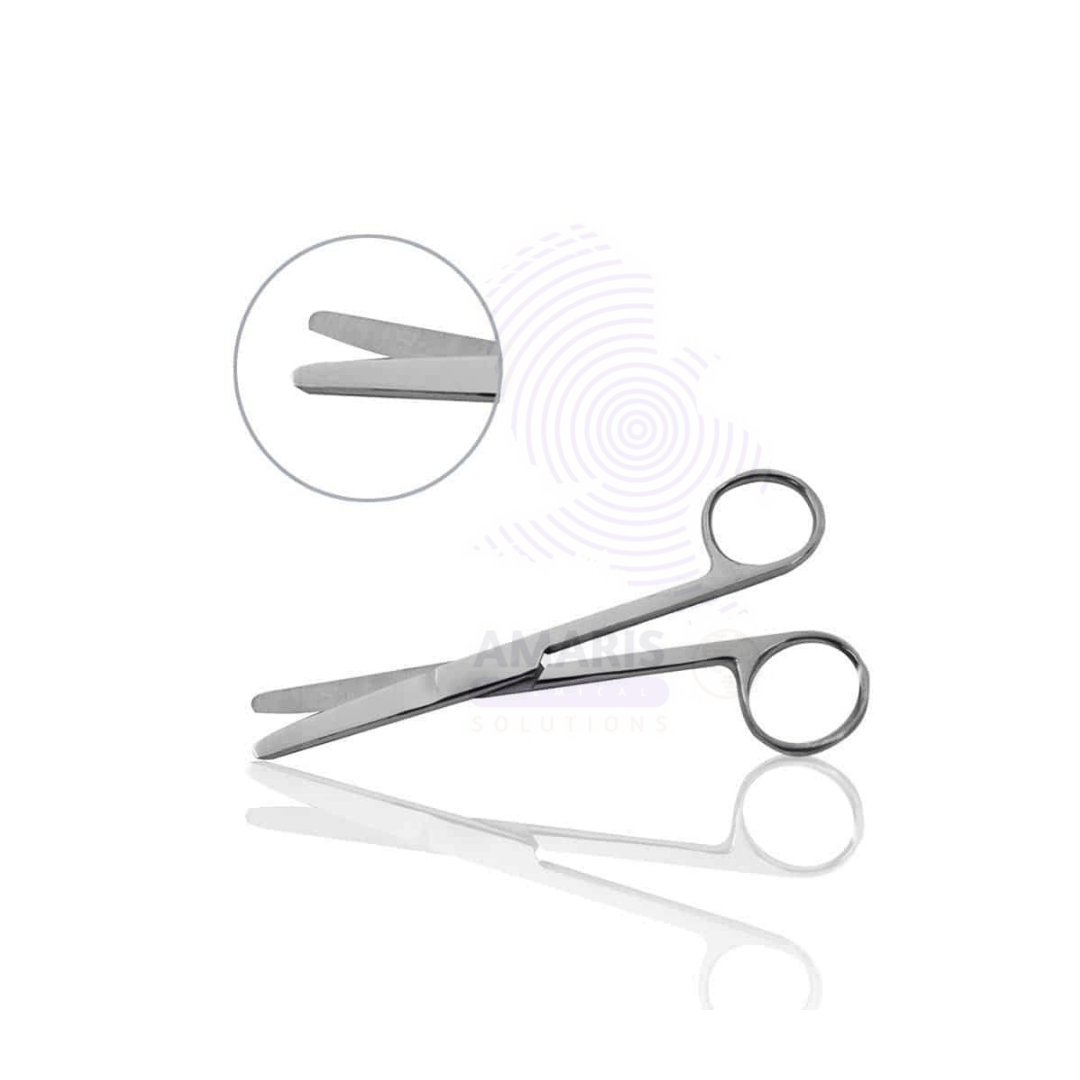
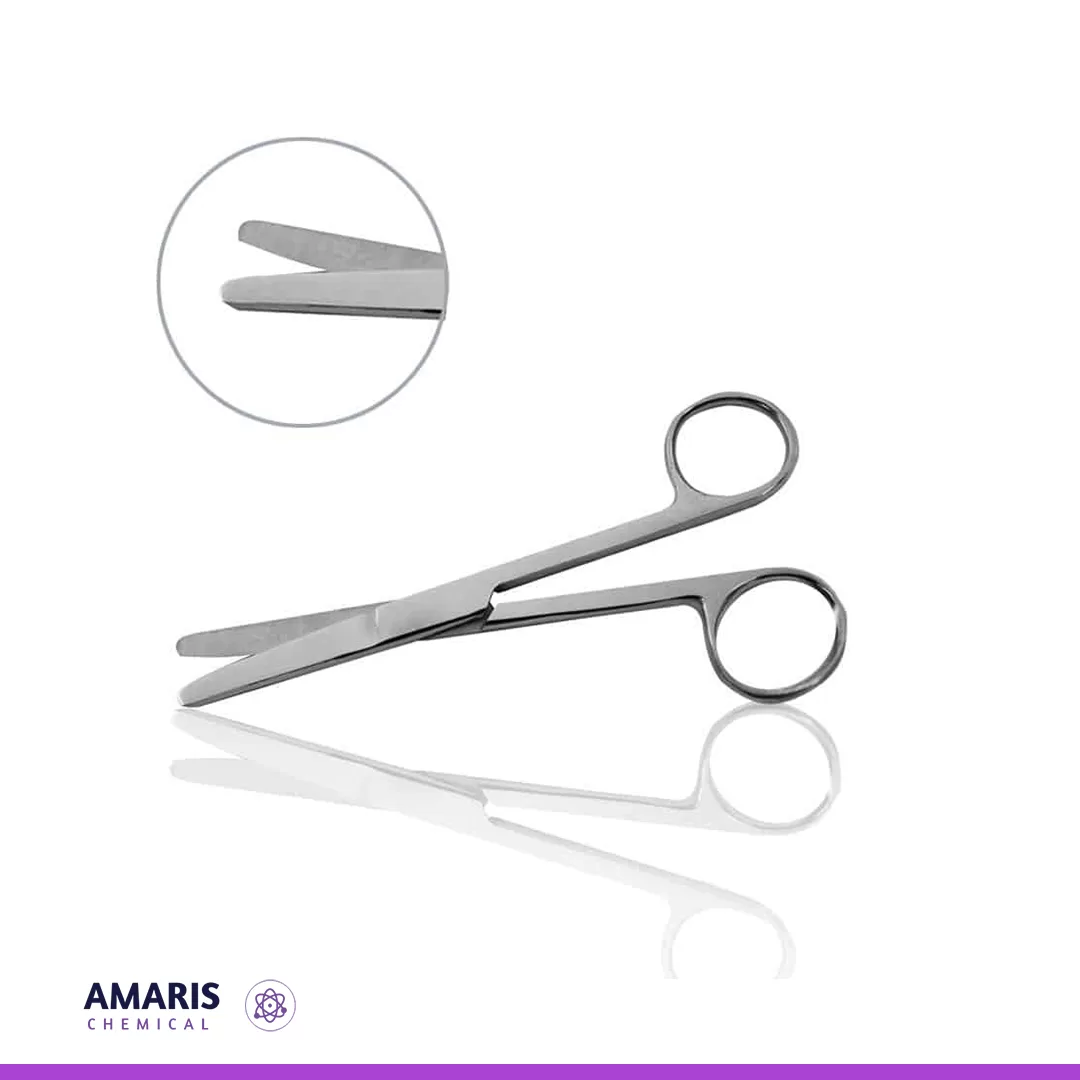
Dissecting forceps
Dissecting forceps are precision instruments resembling tweezers, designed for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues or small objects during dissections or surgical procedures. They typically feature narrow, pointed tips for fine control, allowing users to handle delicate structures with minimal damage. Often made from stainless steel, these tools are essential for separating tissues, removing foreign objects, and working with intricate specimens in biological, medical, or laboratory environments.
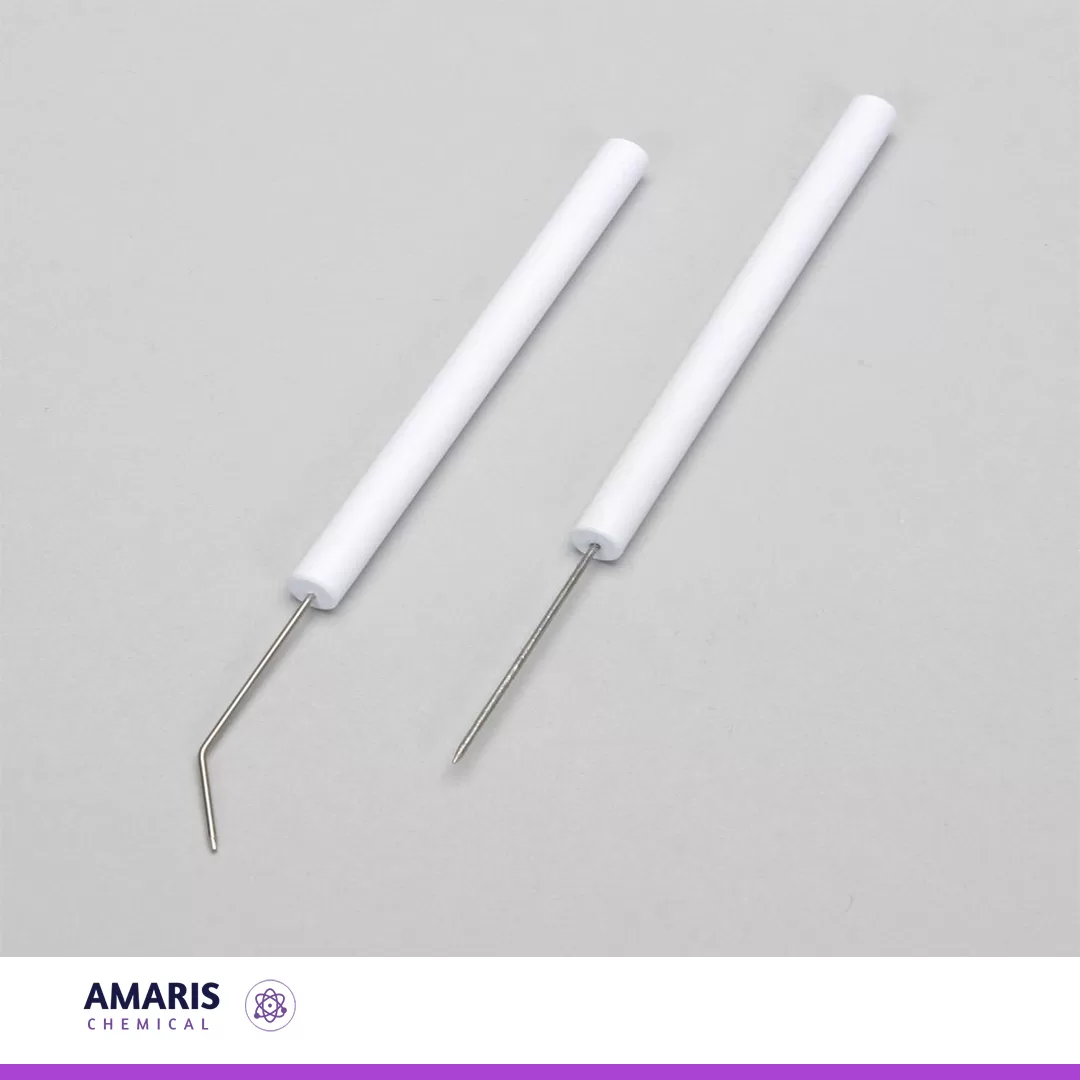
Dissecting needle
A dissecting needle is a slender, pointed tool designed for precision in dissection and manipulation of biological specimens. Typically made from stainless steel, it features a sharp, tapered tip that allows for careful incision and separation of tissues, as well as a fine point for detailed exploration of structures. Some dissecting needles may have a curved or angled design to enhance accessibility in tight spaces. Commonly used in biology, anatomy, and medical labs, this tool is essential for researchers and students alike, aiding in the study and analysis of specimens with accuracy and control.
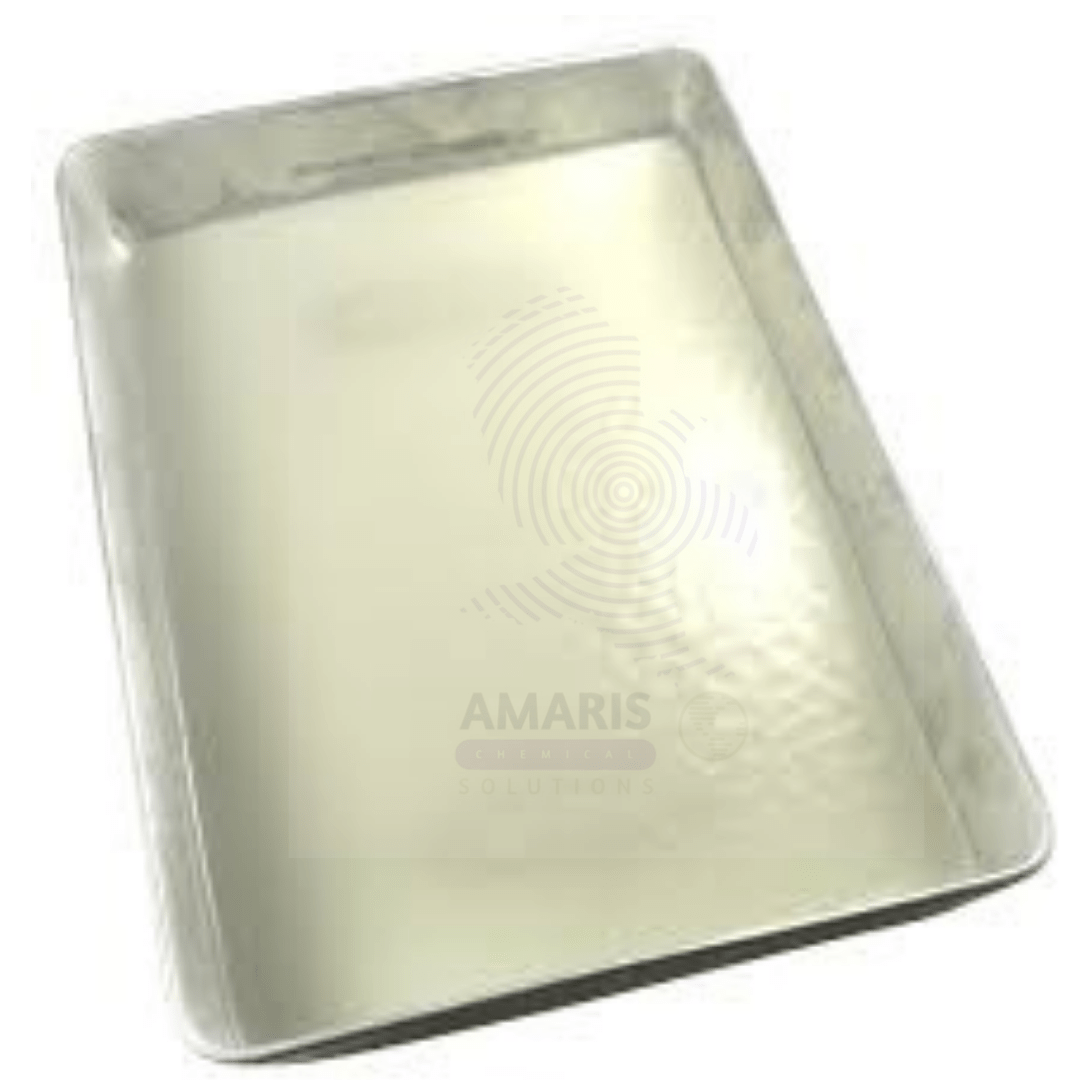
Dissecting pan with wax
A dissecting pan with wax is a specialized laboratory tool designed for use in biological and anatomical dissections. It features a shallow, rectangular container lined with a layer of wax, providing a stable and supportive base for holding specimens securely during dissection. The wax layer retains moisture, preventing specimens from drying out, while also allowing for easy manipulation and positioning. The pan often includes compartments or edges that help organize dissection tools and keep specimens in place. Its durable and easy-to-clean surface makes it suitable for repeated use in educational settings and research laboratories, facilitating hands-on learning and detailed anatomical exploration.
Dissecting-board-soft-board
A Dissecting Board (Soft Board) is a specialized laboratory tool designed to provide a soft, cushioned surface for biological dissections. Typically made from materials like cork, rubber, or other soft polymers, it allows for easy pinning and securing of specimens during dissection. The soft texture protects delicate instruments from dulling, prevents damage to the work surface, and ensures a stable environment for detailed anatomical study. Ideal for use in biology labs, medical research, and educational settings, it supports both precision and safety in dissection procedures.
Distillation apparatus
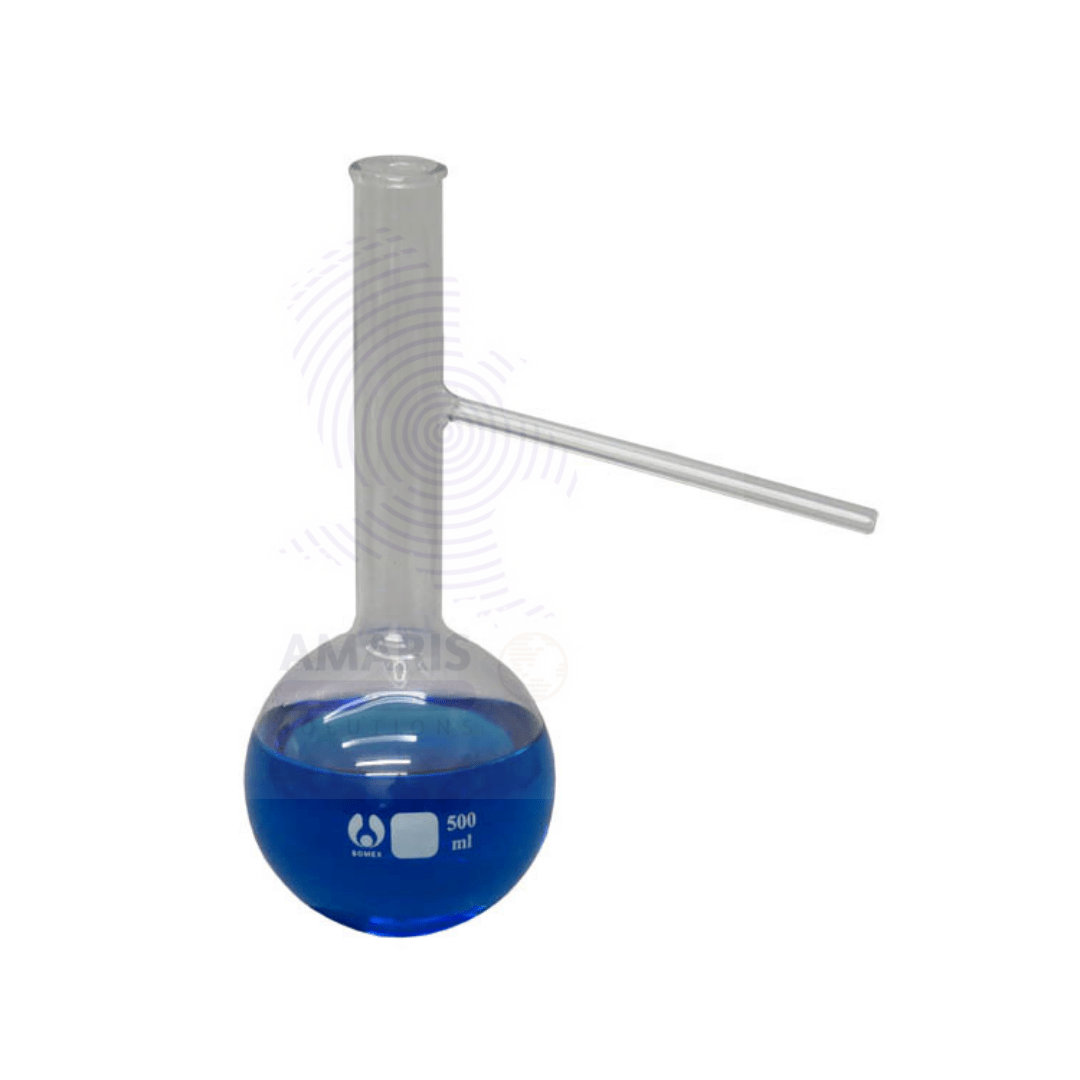
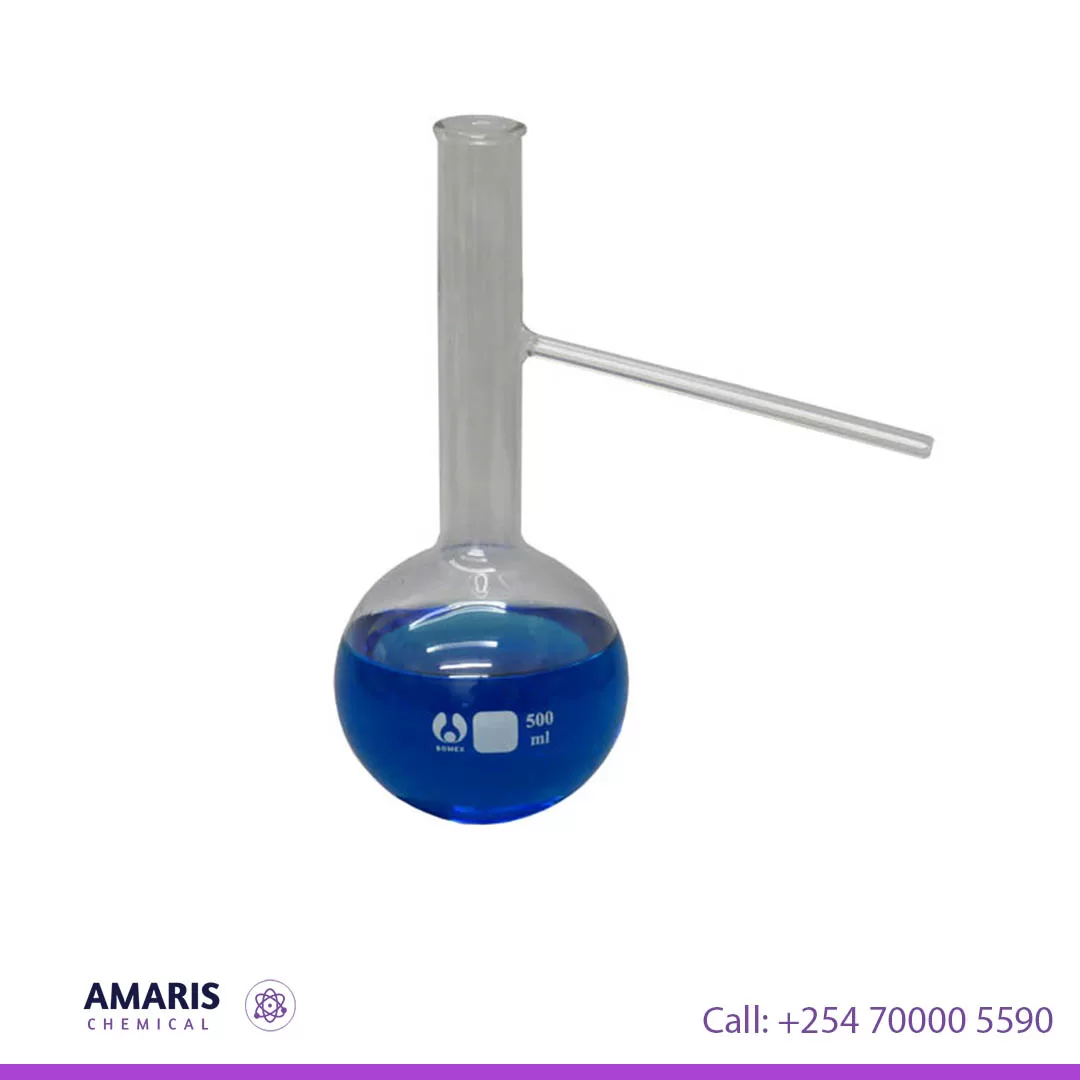
A distillation apparatus is a laboratory setup used to separate and purify liquids based on their boiling points. It typically consists of a distillation flask, where the liquid mixture is heated until the more volatile components evaporate. The vapor then passes through a condenser, which cools it back into a liquid state. This condensed liquid, called the distillate, is collected in a receiver flask. A thermometer is often placed near the outlet of the distillation flask to monitor the temperature of the vapor, ensuring precise control over the separation process. This apparatus is widely utilized for tasks like purifying chemicals, recovering solvents, and separating liquid mixtures in chemical research and industrial applications.
Distillation Flask with side arm
Distilled Water 20 liters
Distilled water is water that has been purified through a process of distillation. Distillation involves boiling water and then condensing the steam back into liquid form, leaving behind impurities and contaminants. This process removes minerals, salts, and other substances, resulting in water that is nearly pure H2O. Distilled water is commonly used in laboratory settings, in medical procedures, and in some household appliances such as steam irons and humidifiers. It's also often used in automotive cooling systems and in certain types of aquariums. However, because it lacks minerals that are beneficial to health, long-term consumption of distilled water may not be ideal for human consumption.