Your cart is currently empty!
Blog
-

The Role of Phosphoric Acid in Industry: Applications and Innovations
Phosphoric acid (H₃PO₄) is a vital inorganic acid with widespread industrial applications. Known for its versatility, this chemical compound plays a crucial role in manufacturing, agriculture, food processing, and even pharmaceuticals. Its unique properties make it indispensable in various sectors, driving innovation and efficiency.
Industrial Applications of Phosphoric Acid
- Fertilizer Production
The largest consumer of phosphoric acid is the agricultural sector, where it is a key ingredient in phosphate-based fertilizers. These fertilizers, such as monoammonium phosphate (MAP) and diammonium phosphate (DAP), enhance soil fertility and crop yield, making phosphoric acid essential for global food production. - Food and Beverage Industry
Phosphoric acid serves as an acidity regulator in soft drinks, particularly in colas, giving them their tangy taste. It is also used in food processing as a preservative and pH adjuster in products like dairy, processed meats, and baked goods. - Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care
In the pharmaceutical industry, phosphoric acid is used to produce medicines, including anti-nausea drugs and dental products like toothpaste, where it helps remove plaque and tartar. It is also found in skin care formulations, contributing to exfoliation and pH balance. - Metal Treatment and Manufacturing
Phosphoric acid is widely used in metal treatment processes, such as rust removal and surface preparation before painting or coating. It plays a crucial role in phosphate coatings that prevent corrosion and improve adhesion in automotive and industrial applications. - Water Treatment and Detergents
As a component in water treatment chemicals, phosphoric acid helps control pH levels and prevent scaling in boilers and cooling systems. Additionally, it is a key ingredient in detergents and cleaning agents, enhancing their effectiveness in removing stains and grease.
Innovations in Phosphoric Acid Applications
Recent advancements in green chemistry have led to more sustainable production methods for phosphoric acid, reducing energy consumption and waste byproducts. Researchers are also exploring bio-based alternatives and recycling processes to recover phosphoric acid from waste streams, promoting circular economy principles.
From agriculture to high-tech industries, phosphoric acid remains an irreplaceable chemical driving innovation and efficiency. As industries evolve, the demand for cleaner, more sustainable production methods will continue shaping the future of phosphoric acid applications.
- Fertilizer Production
-

Understanding Silica Gel: How It Works and Why You Need It
Silica gel is a common yet often overlooked desiccant used to control moisture in various applications. You’ve likely encountered those small packets inside new shoes, electronics, or medicine bottles. But how does silica gel work, and why is it essential?
What Is Silica Gel?
Silica gel is a porous form of silicon dioxide (SiO₂) that has a high affinity for moisture. Unlike what its name suggests, it isn’t a gel but a solid substance that appears as small beads. These beads contain microscopic pores that absorb and hold moisture, preventing damage caused by humidity.
How Does Silica Gel Work?
Silica gel functions through a process called adsorption. This means that instead of absorbing moisture like a sponge, it captures water molecules on its surface. Due to its large surface area, silica gel can trap significant amounts of water, making it highly effective in reducing humidity.
Why Do You Need Silica Gel?
- Protects Electronics – Moisture can corrode metal components and damage circuit boards. Silica gel prevents condensation, ensuring your devices remain functional.
- Preserves Pharmaceuticals – Medications can degrade due to excess moisture. Silica gel packets help maintain drug stability and efficacy.
- Prevents Mold and Mildew – In storage areas, excess humidity can lead to mold growth. Placing silica gel packets in containers, bags, or cabinets helps keep spaces dry.
- Extends Shelf Life of Food Products – In packaged goods like snacks and dried foods, moisture can cause spoilage. Silica gel helps maintain freshness.
- Protects Documents and Photographs – Important papers and old photographs are vulnerable to moisture damage. Silica gel keeps them safe from deterioration.
Reusing Silica Gel
Silica gel can be reused by drying it out. Simply place it in an oven at 250°F (120°C) for a few hours to remove absorbed moisture.
Conclusion
Silica gel is a powerful moisture-control solution that protects valuable items from humidity-related damage. Whether for electronics, food, or storage, having silica gel on hand ensures long-term protection and preservation.
-

Understanding Sodium Sulphide: Applications, Benefits, and Safety Considerations
Sodium sulphide (Na2S) is a versatile chemical compound widely used across multiple industries. Known for its strong reducing properties and ability to react with various substances, it plays a crucial role in industrial processes. This article explores its applications, benefits, and essential safety measures.
Applications of Sodium Sulphide
Sodium sulphide is widely utilized in different sectors, including:
- Leather Industry – Used in the dehairing process of hides and skins, making it an essential compound in leather tanning.
- Pulp and Paper Industry – Plays a key role in the Kraft process, helping break down wood fibers for paper production.
- Textile Industry – Acts as a reducing agent in dyeing applications, particularly for sulfur dyes.
- Water Treatment – Used to remove heavy metals from wastewater, making it valuable in environmental management.
- Ore Processing – Involved in the flotation process of metal ores such as copper and lead.
- Chemical Manufacturing – Serves as a precursor in the production of sulfur-based chemicals.
Benefits of Sodium Sulphide
Sodium sulphide offers several advantages that contribute to its widespread use:
- Efficiency – Its strong reducing properties enhance industrial chemical reactions.
- Cost-Effectiveness – Available at a relatively low cost, making it a practical choice for large-scale operations.
- Versatility – Applicable in multiple industries, ranging from textiles to metallurgy.
- Environmental Utility – Helps in wastewater treatment by precipitating heavy metals, reducing pollution.
Safety Considerations
While highly beneficial, sodium sulphide requires careful handling due to its potential hazards:
- Corrosive Nature – Can cause skin burns and eye irritation upon contact.
- Toxicity – Releases hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gas in moist conditions, which is highly toxic and has a foul odor.
- Proper Storage – Should be kept in airtight containers away from moisture and acids.
- Protective Measures – Use personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and masks when handling.
- Ventilation – Work in well-ventilated areas to prevent inhalation of harmful fumes.
Conclusion
Sodium sulphide is a crucial industrial chemical with diverse applications and significant benefits. However, strict safety protocols must be followed to ensure its safe handling and use. Understanding its properties and risks allows industries to maximize its utility while minimizing hazards.
-
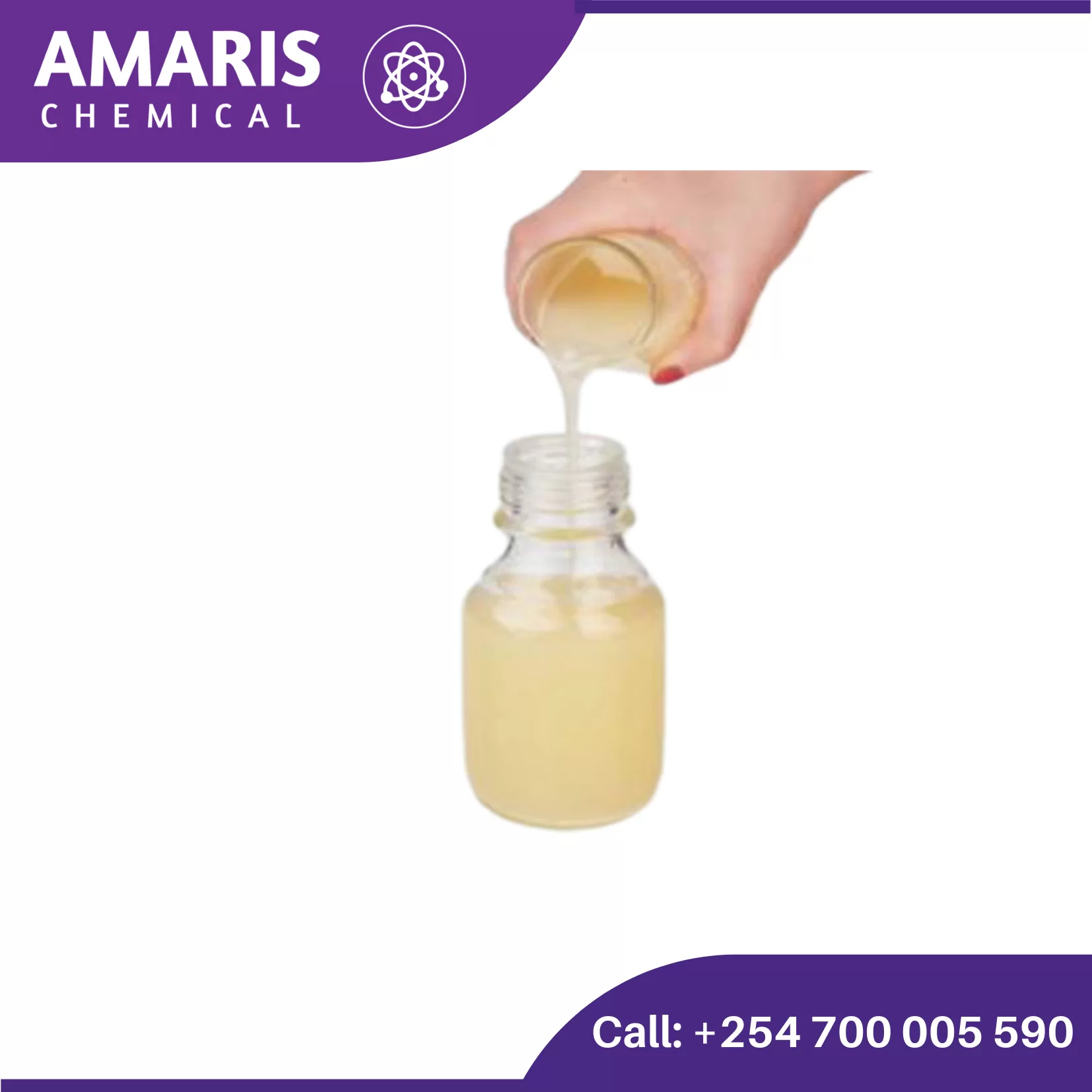
Understanding Defoamers: The Essential Guide to Foam Control in Industrial Applications
Foam can be a major issue in industrial processes, affecting efficiency, quality, and equipment functionality. Whether in food processing, wastewater treatment, or chemical manufacturing, excessive foam can cause serious operational disruptions. This is where defoamers play a crucial role.
What Are Defoamers?
Defoamers, also known as anti-foaming agents, are chemical additives that reduce or prevent foam formation in industrial processes. They work by destabilizing foam bubbles, causing them to collapse and preventing their regeneration. Defoamers are essential in industries where foam can interfere with production, such as pulp and paper, coatings, textiles, and pharmaceuticals.
How Do Defoamers Work?
Defoamers operate through three primary mechanisms:
- Breaking Foam Bubbles: They weaken the surface tension of foam bubbles, making them burst.
- Preventing Bubble Formation: They reduce the likelihood of foam forming by modifying liquid properties.
- Spreading and Coalescence: They spread over the foam surface, causing bubbles to merge and collapse.
Types of Defoamers
Defoamers come in various formulations to suit specific industrial needs. The main types include:
- Oil-Based Defoamers: These contain oils like mineral or vegetable oil and are effective in non-aqueous systems.
- Silicone-Based Defoamers: Highly effective in many industries, these defoamers work well at low concentrations.
- Powdered Defoamers: Used in powder-based processes, such as cement manufacturing and detergents.
- Water-Based Defoamers: These are eco-friendly and often used in food processing and wastewater treatment.
Applications of Defoamers
Defoamers are widely used across industries, including:
- Wastewater Treatment: Prevents foam overflow and improves efficiency in aeration tanks.
- Food & Beverage: Ensures smooth processing in fermentation and dairy production.
- Paints & Coatings: Reduces surface defects caused by foam in coatings and adhesives.
- Chemical Processing: Enhances mixing and prevents disruptions in manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Defoamer
Selecting the right defoamer depends on factors such as process conditions, compatibility with the system, and environmental impact. Silicone-based defoamers, for instance, offer excellent performance in high-temperature applications, while water-based options are preferred for food-safe processes.
Conclusion
Defoamers are indispensable in industrial applications where foam can hinder productivity and quality. Understanding their types and functions helps industries optimize performance and maintain smooth operations. By choosing the right defoamer, businesses can improve efficiency and reduce downtime effectively.
-

Ferric Chloride: Key Insights into Its Properties and Environmental Impact
Ferric chloride, commonly known as iron(III) chloride (FeCl₃), is an important chemical compound with diverse applications in industries ranging from water treatment to electronics. As a versatile chemical, it offers both significant benefits and challenges, particularly regarding its properties and environmental impact.
Properties of Ferric Chloride
Ferric chloride is a dark, crystalline solid, typically brownish-yellow in color. It is highly soluble in water, forming a strongly acidic solution. This property makes it effective in various chemical processes. The compound plays a crucial role as a flocculant in water treatment, where it is used to remove impurities such as suspended solids, phosphates, and other contaminants. Its ability to act as a coagulant makes it essential in municipal water and wastewater treatment plants.
Ferric chloride is also employed in the production of printed circuit boards (PCBs), where it is used to etch copper to create intricate electronic designs. In addition, it serves as a catalyst in chemical reactions, including the production of certain organic compounds.
Environmental Impact
While ferric chloride is highly effective in various industrial applications, its environmental impact should not be overlooked. The disposal of ferric chloride waste, especially from water treatment processes, poses significant challenges. If not treated properly, the chemical can contribute to soil and water pollution due to its acidity and high metal content. Excessive iron can lead to the contamination of water bodies, disturbing aquatic ecosystems.
Moreover, ferric chloride is a corrosive substance, and improper handling or accidental spills can cause damage to the surrounding environment and pose risks to human health. For example, inhalation of ferric chloride fumes can irritate the respiratory system, while skin contact may cause burns or irritation.
Sustainable Alternatives
To mitigate the environmental risks associated with ferric chloride, researchers are exploring more sustainable alternatives for water treatment and other applications. These include less toxic coagulants and greener etching methods for PCB production. Moreover, better waste management practices, including recycling and neutralization of ferric chloride solutions, are crucial to reducing the environmental footprint of this chemical.
In conclusion, ferric chloride is a vital industrial compound with broad applications. However, its environmental impact must be managed carefully through sustainable practices and proper waste disposal methods to minimize harm to ecosystems and human health.
-
Understanding Isopropyl Alcohol: Benefits, Uses, and Best Practices
Isopropyl alcohol (IPA), also known as rubbing alcohol, is a versatile chemical compound that plays a vital role in both household and industrial settings. It is a colorless, flammable liquid with a strong odor and is commonly used as a disinfectant, solvent, and antiseptic. In this blog, we will explore its benefits, uses, and best practices for handling isopropyl alcohol.
Benefits of Isopropyl Alcohol
One of the main benefits of isopropyl alcohol is its effectiveness as an antiseptic. It is commonly used for disinfecting surfaces and sanitizing hands, particularly in environments where cleanliness is critical. Isopropyl alcohol can kill bacteria, fungi, and viruses, making it an essential tool in healthcare settings, particularly in hospitals and clinics.
Another significant benefit of IPA is its use as a solvent. It dissolves oils, greases, and resins, making it a go-to solution for cleaning electronics, removing ink stains, and even dissolving adhesives. Its ability to evaporate quickly ensures that surfaces dry without leaving residue, making it ideal for cleaning delicate components such as circuit boards and screens.
Common Uses of Isopropyl Alcohol
The versatility of IPA extends beyond medical and industrial applications. It is widely used in personal care products like hand sanitizers, cosmetics, and disinfecting wipes. Additionally, it serves as a common ingredient in the formulation of some over-the-counter medications.
Isopropyl alcohol is also effective for cleaning surfaces in the home. It can be used to remove fingerprints, clean mirrors, and shine glass. It’s even useful for removing sticky residues from labels and stickers.
Best Practices for Handling Isopropyl Alcohol
Despite its many uses, isopropyl alcohol is a highly flammable substance and should be handled with care. Always store it in a cool, well-ventilated area away from heat sources or open flames. When using it for cleaning, ensure that the room is adequately ventilated to prevent inhalation of fumes.
For health and safety, always use IPA in moderation and avoid prolonged skin contact. In case of skin irritation, rinse thoroughly with water. When using it as a disinfectant or antiseptic, ensure it is used in concentrations of 60% to 90% for maximum effectiveness.
Conclusion
Isopropyl alcohol is an essential chemical in both domestic and industrial applications. Its ability to disinfect, clean, and dissolve makes it a must-have in many households and businesses. By following the best practices for handling and storage, you can safely take advantage of its many benefits.
-

Understanding Potassium Nitrate: Benefits, Uses, and Safety Considerations
Potassium nitrate (KNO₃) is a versatile and widely used chemical compound with a variety of applications in both industrial and agricultural sectors. It plays a crucial role in various fields, from fertilizers to food preservation, explosives, and even healthcare. However, like all chemicals, it’s essential to understand its benefits, uses, and safety precautions to handle it properly.
Benefits of Potassium Nitrate
One of the primary benefits of potassium nitrate is its function as a key component in fertilizers. It provides essential nutrients—potassium and nitrogen—both critical for plant growth. Potassium enhances root development and disease resistance, while nitrogen promotes healthy foliage and overall plant vitality. This makes potassium nitrate an invaluable resource in agriculture, especially for growing fruits, vegetables, and other crops.
In addition, potassium nitrate is used in food preservation, particularly in cured meats like bacon and ham. It acts as a preservative by inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria and helping to retain color and flavor. This characteristic is what allows potassium nitrate to be a staple in the food industry.
Potassium nitrate also has applications in pyrotechnics, where it is a vital ingredient in the production of gunpowder, fireworks, and other explosive materials. It serves as an oxidizing agent, enabling the combustion process necessary for these items to function.
Uses of Potassium Nitrate
- Agriculture: Used as a fertilizer to supply essential nutrients for plant growth.
- Food Industry: Helps in curing meats and preserving food.
- Pyrotechnics & Explosives: A key component in gunpowder and fireworks.
- Healthcare: Sometimes used in dental care products, like toothpaste, to reduce tooth sensitivity.
Safety Considerations
While potassium nitrate is valuable in many industries, safety is a top priority when handling it. As a strong oxidizing agent, potassium nitrate can react violently with combustible materials, increasing the risk of fires or explosions. It is important to store it in a cool, dry place, away from any flammable substances. Always wear protective equipment such as gloves and goggles when handling the compound, and follow proper disposal guidelines.
In conclusion, potassium nitrate is a multifaceted chemical that offers significant benefits across a range of applications. Understanding its uses and safety protocols ensures its effective and safe incorporation into both industrial and everyday uses
-

Ferrous Sulphate: A Comprehensive Overview of Its Importance in Nutritional Supplements and Soil Health
Ferrous sulphate, also known as iron(II) sulfate, is a widely used compound with significant applications in both nutrition and agriculture. This versatile chemical plays a pivotal role in addressing iron deficiencies in human health and improving soil fertility for better agricultural productivity.
Nutritional Supplements
Iron is an essential mineral required by the body for the production of hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that transports oxygen throughout the body. One of the most common forms of iron supplements is ferrous sulphate, which is highly effective in treating iron deficiency anemia. It is available in various forms, including tablets, liquids, and capsules, making it convenient for individuals to meet their daily iron requirements.
The bioavailability of iron in ferrous sulphate is relatively high, meaning the body can absorb and utilize it efficiently. This makes it a preferred choice for treating anemia, particularly in pregnant women, children, and individuals with low iron levels. Iron plays a vital role in maintaining energy levels, supporting the immune system, and promoting cognitive function. By replenishing iron stores, ferrous sulphate helps to combat fatigue, weakness, and other symptoms associated with iron deficiency.
Soil Health and Agriculture
In addition to its role in human health, ferrous sulphate is also valuable in agriculture. It is commonly used as a soil amendment to address iron deficiencies in plants. Iron is an essential nutrient for plants, contributing to chlorophyll formation and overall plant growth. However, certain soils, particularly those with high pH levels or poor iron availability, may result in chlorosis (yellowing of leaves) in plants due to insufficient iron uptake.
Ferrous sulphate is used to correct this deficiency by providing plants with a readily available form of iron. It is often applied to the soil or used as a foliar spray to deliver iron directly to the leaves. This helps to promote healthy plant growth, enhance photosynthesis, and improve crop yields. Additionally, ferrous sulphate can be used in the treatment of certain plant diseases that are related to iron deficiencies, such as iron chlorosis in ornamental plants and crops like citrus and roses.
Conclusion
Ferrous sulphate is a crucial compound that serves two main functions in modern society: improving human health through iron supplementation and supporting soil health for agricultural success. Its versatility in both medicine and agriculture makes it a valuable resource, contributing to better nutrition and enhanced crop production. Whether as a dietary supplement or a soil treatment, ferrous sulphate continues to play a vital role in enhancing the well-being of both individuals and the environment.
-

The Ultimate Guide to Hydrogen Peroxide 35%: Applications and Precautions
Hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) is a powerful and versatile chemical with a variety of applications, from medical uses to industrial processes. The 35% concentration of hydrogen peroxide, often referred to as “food grade” hydrogen peroxide, is notably stronger than the typical 3% solution found in stores. This potency makes it incredibly effective in certain applications, but it also requires careful handling and awareness of safety precautions.
Applications of 35% Hydrogen Peroxide
- Disinfection and Sanitization
Hydrogen peroxide 35% is a potent disinfectant, effective at killing bacteria, viruses, and fungi. It is widely used in hospitals, laboratories, and even in home cleaning. Diluted to lower concentrations, it can be used for disinfecting countertops, utensils, and medical equipment. - Water Treatment
In water treatment, hydrogen peroxide is used to purify water by breaking down contaminants and removing odors. It’s an eco-friendly alternative to chlorine, particularly in large-scale industrial processes. - Food Processing
Though not directly consumed, 35% hydrogen peroxide is used in food-grade applications such as sanitizing surfaces, equipment, and even fruits and vegetables. It helps in reducing pesticide residues and bacteria, ensuring food safety. - Wound Care
In medical settings, diluted hydrogen peroxide is often used to clean wounds due to its antibacterial properties. However, for professional use, 35% hydrogen peroxide should be diluted significantly to avoid tissue damage. - Teeth Whitening
Hydrogen peroxide is commonly included in teeth whitening products due to its bleaching properties. In professional treatments, a diluted form of 35% hydrogen peroxide is applied to help remove stains from teeth, brightening smiles.
Precautions
While hydrogen peroxide 35% has many benefits, it is highly corrosive and can cause serious harm if not handled properly. Here are essential precautions to follow:
- Wear Protective Gear
Always wear gloves, goggles, and protective clothing when working with concentrated hydrogen peroxide. The chemical can cause severe skin burns and eye damage. - Proper Storage
Store 35% hydrogen peroxide in a cool, dry, and dark place, away from direct sunlight and heat sources. It should be kept in containers made of compatible materials such as plastic or stainless steel, as it reacts with metals. - Dilution Is Key
For most household and medical uses, hydrogen peroxide should be diluted. Never use it in its concentrated form on skin, wounds, or surfaces without proper dilution guidelines. - Avoid Mixing
Never mix hydrogen peroxide with other chemicals, especially vinegar or ammonia, as this can lead to dangerous reactions.
In conclusion, hydrogen peroxide 35% is a powerful chemical with vast potential across various industries. However, it is important to approach it with caution, respect its hazards, and follow safety guidelines to ensure it is used effectively and safely.
- Disinfection and Sanitization
-

Distilled Water vs. Tap Water: Which Is the Better Choice for Your Health?
When it comes to choosing water for drinking and hydration, many people wonder whether distilled water or tap water is the healthier option. While both are commonly consumed, understanding the differences between them can help you make an informed decision for your health.
What is Distilled Water?
Distilled water is created by boiling water to produce steam, which is then cooled and condensed back into water. This process removes impurities, such as minerals, chemicals, and contaminants, leaving behind pure H2O. Because it is so thoroughly purified, distilled water is free from any dissolved solids.
What is Tap Water?
Tap water, on the other hand, is sourced from local reservoirs, rivers, or groundwater and undergoes treatment processes, including filtration and disinfection, to ensure it’s safe for consumption. The specific quality of tap water can vary greatly depending on where you live, but it typically contains a variety of minerals like calcium and magnesium, as well as potentially some trace chemicals that may have been used in the treatment process.
Health Benefits of Distilled Water
Distilled water is often touted for its purity. For individuals living in areas with poor water quality or those who are sensitive to minerals and chemicals, distilled water can be a safer option. It’s free from contaminants, chlorine, lead, and other substances that could negatively affect your health. Additionally, distilled water is often recommended in medical settings and for people using specific appliances that require mineral-free water.
However, a downside to distilled water is that it lacks essential minerals, such as calcium and magnesium, which are beneficial for the body. These minerals help in maintaining strong bones, heart health, and overall well-being.
Health Benefits of Tap Water
Tap water, though not as pure as distilled water, can provide essential minerals that the body needs for daily function. These include calcium, magnesium, and potassium, which support hydration and electrolyte balance. In many regions, tap water is regularly tested and treated to meet strict safety standards, making it a reliable source of hydration for most people.
However, depending on where you live, tap water might contain trace amounts of chlorine, fluoride, and heavy metals, which can cause health issues over time if consumed in large quantities.
Which Is the Better Choice?
The decision between distilled water and tap water comes down to individual needs. If you live in an area with high water quality, tap water may be your best option, providing both hydration and minerals. However, if you’re concerned about contaminants or prefer purer water, distilled water may be more suitable, though it’s important to supplement your diet with necessary minerals from other sources.